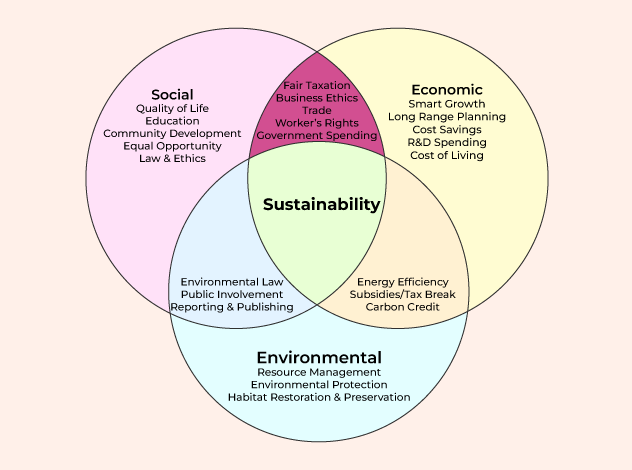
⚖️ Principles of Sustainable Development
1. 🌍 Environmental Protection
Protecting and restoring ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources.
2. 🤝 Social Equity
Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all people.
3. 💼 Economic Viability
Creating economic systems that are sustainable and benefit society.
4. 🔄 Intergenerational Equity
Meeting present needs without compromising future generations.
5. 🌐 Precautionary Principle
Taking preventive action when environmental harm is possible, even without complete scientific certainty.
6. 👥 Public Participation
Involving all stakeholders in decision-making processes.
7. 🔗 Integration
Integrating environmental, social, and economic considerations in all decisions.
8. 📊 Accountability
Taking responsibility for environmental and social impacts of actions.
9. ♻️ Polluter Pays
Those who cause pollution should bear the costs of managing it.
10. 🌱 Sustainable Consumption
Using resources efficiently and minimizing waste.
11. 🏘️ Livable Communities
Creating communities that are healthy, safe, and vibrant.
12. 🔬 Science-Based Decisions
Using scientific knowledge and traditional wisdom in planning.
🌡️ Climate Change Mitigation
Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and helps combat global warming.
💧 Resource Security
Ensures availability of clean water, food, and energy for future.
🌳 Biodiversity Protection
Preserves ecosystems and species essential for life on Earth.
👨👩👧👦 Improved Quality of Life
Creates healthier, safer communities with better living conditions.
💼 Economic Stability
Promotes long-term economic growth without environmental degradation.
⚖️ Social Justice
Reduces inequality and ensures fair access to resources.
🏥 Public Health
Reduces pollution-related diseases and improves overall health.
🔒 Energy Security
Promotes renewable energy reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
🌾 Food Security
Ensures sustainable agriculture for long-term food supply.
🏙️ Urban Sustainability
Creates livable cities with efficient infrastructure and services.
🎓 Education & Awareness
Promotes knowledge about environmental and social responsibility.
🌍 Global Cooperation
Encourages international collaboration on shared challenges.
• Healthier ecosystems and cleaner environment
• More resilient communities
• Reduced poverty and inequality
• Stable economic growth
• Better future for next generations
• Peace and security through resource management
• Irreversible environmental damage
• Resource depletion
• Increased natural disasters
• Social conflicts over resources
• Economic instability
• Health crises