Introduction to Sources of Energy
- Energy enables work and daily activities
- Sources provide heat, light, and power
- Ideal sources are efficient and safe
- Renewable sources are unlimited
- Non-renewable sources are depleting
- Shift to renewables reduces pollution
Types of Sources of Energy

- Renewable: Replenished naturally
- Non-renewable: Limited supply
- Conventional: Long-used (e.g., coal)
- Non-conventional: Newer (e.g., solar)
- Commercial: Bought/sold
- Non-commercial: Freely available
Renewable Sources of Energy
- Replenished naturally in short time
- Inexhaustible and sustainable
- Cause minimal pollution
- Ideal for future generations
- Include solar, wind, hydro, biomass, geothermal
- Promote environmental protection
Solar Energy

- Energy from Sun's heat and light
- Harnessed via photovoltaic panels
- Free, unlimited, and clean
- Useful in remote areas
- No pollution or emissions
- High initial cost; weather dependent
Wind Energy
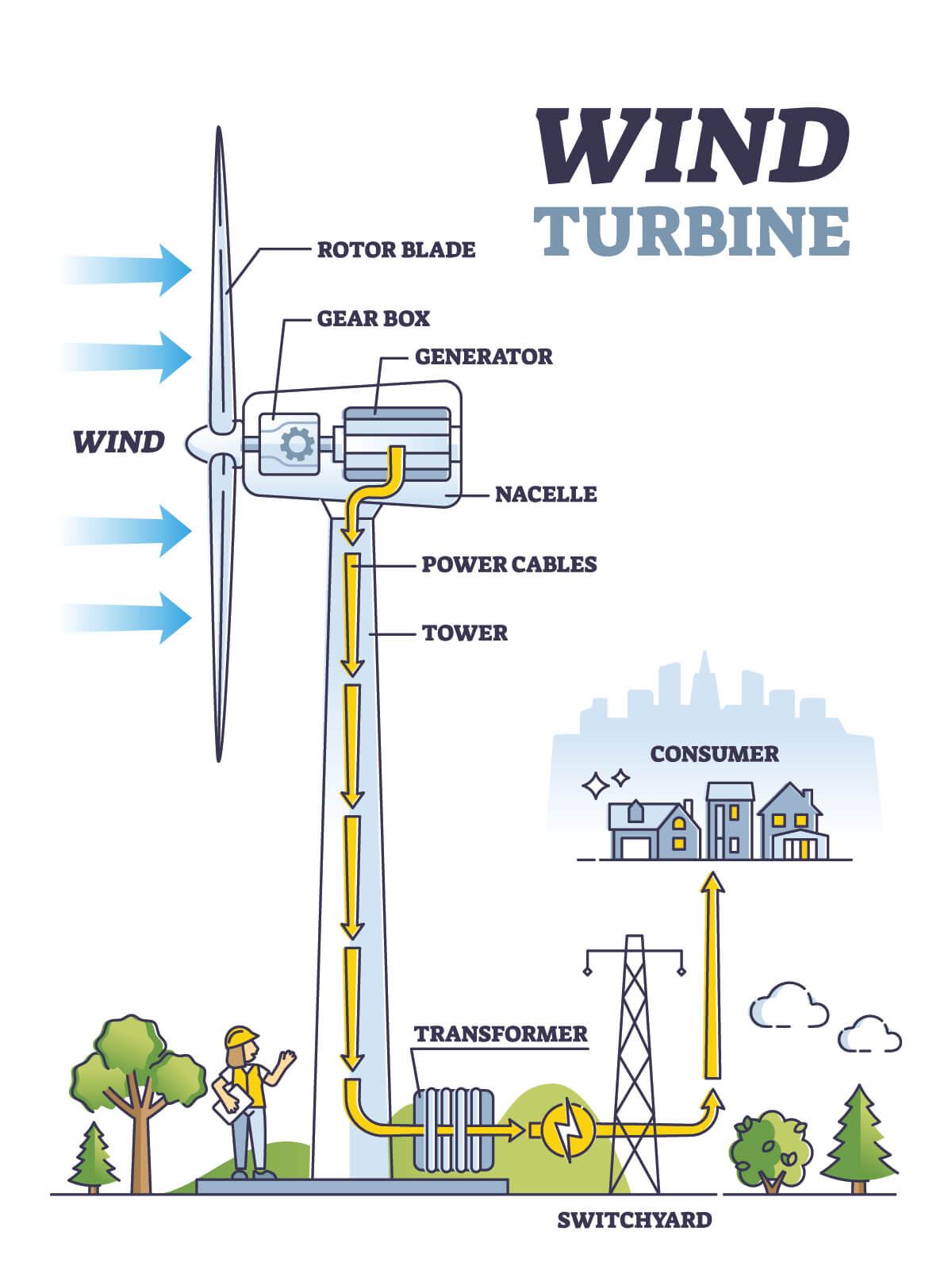
- Kinetic energy from moving air
- Converted using wind turbines
- Clean and renewable
- Low operating costs
- Wind farms in windy locations
- Noise and bird impact issues
Hydro Energy
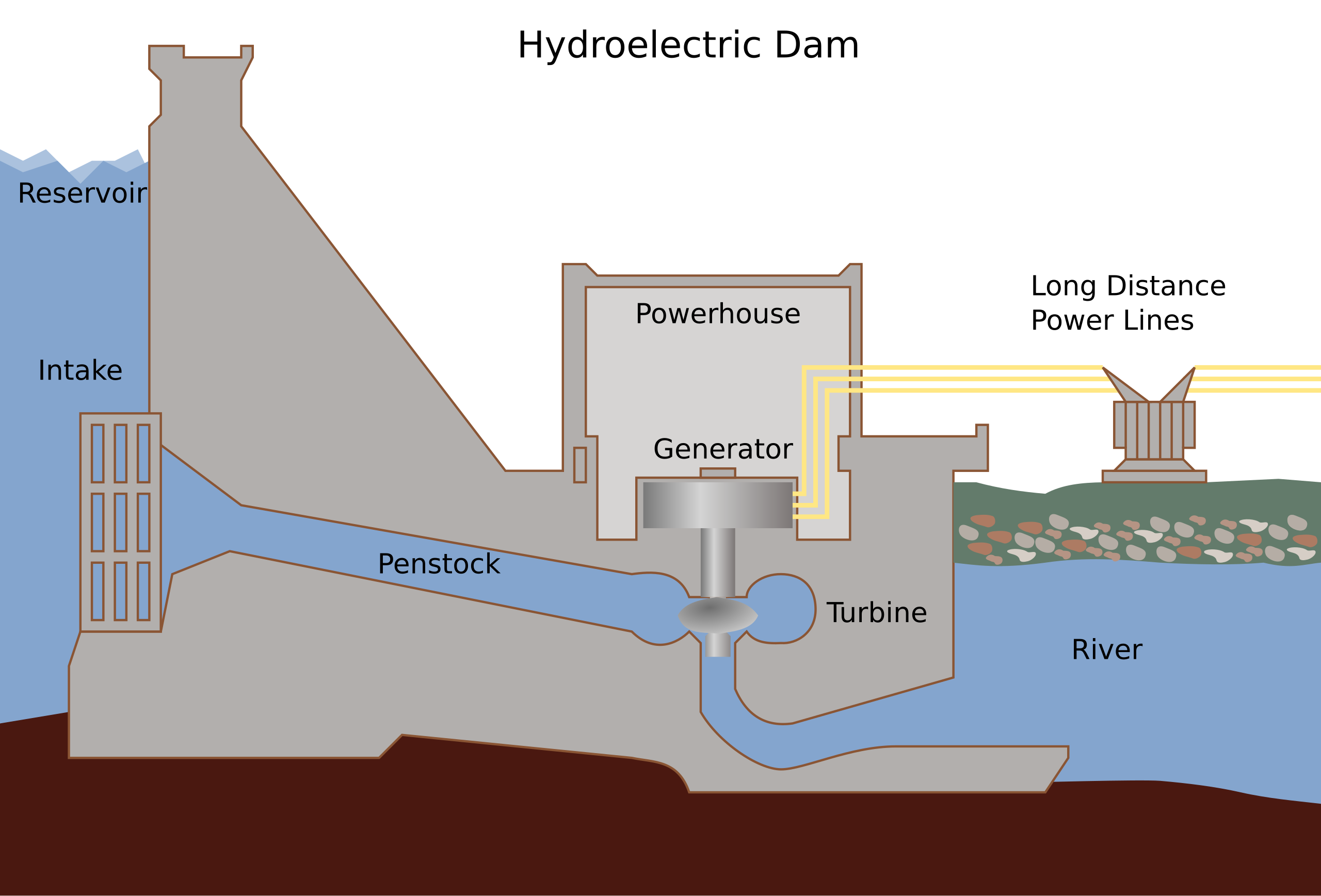
- From flowing or falling water
- Dams turn turbines for electricity
- Clean and renewable
- Aids irrigation and flood control
- Reliable power supply
- High cost; ecosystem disruption
Biomass Energy

- From organic plant/animal waste
- Biogas from anaerobic digestion
- Renewable and reduces waste
- Slurry as fertilizer
- Available in rural areas
- Direct burning causes smoke
Geothermal Energy
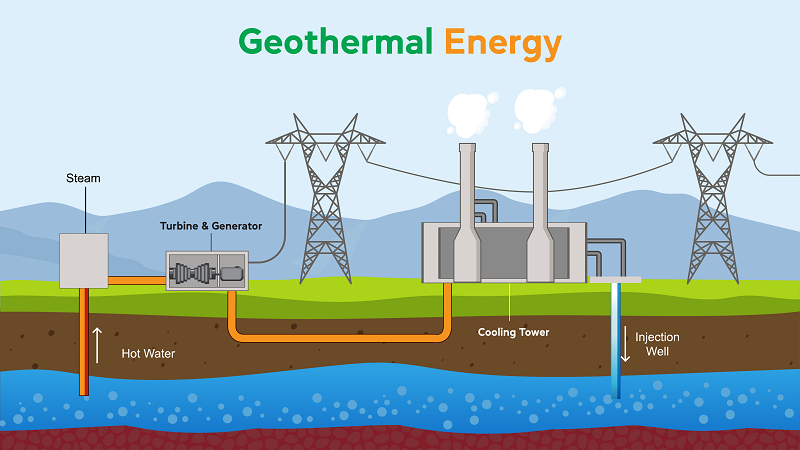
- Heat from Earth's interior
- Steam/hot water drives turbines
- Reliable 24/7 availability
- Clean with low emissions
- Low running costs
- Limited to geothermal sites
Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
- Limited quantities in nature
- Formed over millions of years
- Include fossil fuels and nuclear
- Reliable and high energy output
- Cause pollution and emissions
- Will eventually deplete
Coal

- Solid fossil fuel from buried plants
- Used in thermal power plants
- Abundant reserves
- Key for electricity and steel
- High energy content
- Causes air pollution and CO₂
Petroleum (Crude Oil)
- Liquid fossil fuel from marine organisms
- Refined into fuels and products
- Powers vehicles and industries
- Raw material for plastics
- Easy to transport
- Non-renewable; causes pollution
Natural Gas
- Gaseous fuel, mainly methane
- Used for cooking and power
- Cleanest fossil fuel
- Lower emissions than coal/oil
- Piped or as CNG
- Still non-renewable
Nuclear Energy
- From uranium fission
- Huge energy from small fuel
- No greenhouse gases in operation
- Reliable baseload power
- High efficiency
- Radioactive waste and accident risks